Blood Pressure





Shop a wide range of reliable blood pressure monitors and related products to help you track and manage your health effectively. Find accurate, easy-to-use devices from trusted brands designed for home and clinical use. Buy now to take control of your blood pressure with confidence.
Blood pressure medications are essential for managing hypertension and preventing serious cardiovascular problems. Several popular drugs are commonly prescribed, each with different mechanisms and benefits. Understanding these can help patients and caregivers make informed decisions about therapy.
Aceon (Perindopril) is an ACE inhibitor. It works by relaxing blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure and reduces the heart's workload. Aceon is effective and generally well tolerated, but patients should monitor kidney function and potassium levels.
Adalat (Nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker. It relaxes and widens arteries, improving blood flow. It is useful for managing hypertension and angina. Patients may experience swelling or flushing, but these are usually mild.
Aldactone (Spironolactone) is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It helps remove excess fluid while retaining potassium. Aldactone is often used in resistant hypertension and heart failure. It requires monitoring for potassium levels to avoid hyperkalemia.
Altace (Ramipril) is another ACE inhibitor. Altace is known for its kidney-protective effects, especially in diabetic patients. It lowers blood pressure by inhibiting angiotensin II, leading to vasodilation. Common side effects include cough and dizziness.
Avapro (Irbesartan) is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). It blocks the effects of angiotensin II, helping to relax blood vessels. Avapro is effective for treating high blood pressure and protecting the kidneys. ARBs tend to cause fewer coughs compared to ACE inhibitors.
Beloc (Metoprolol) is a beta-blocker. It reduces heart rate and cardiac output, lowering blood pressure. Beloc also helps manage angina and arrhythmias. Common side effects include fatigue and dizziness, especially during dose changes.
Benicar (Olmesartan) is an ARB known for potent blood pressure control. It is well tolerated but requires regular monitoring of kidney function and electrolytes. Benicar is useful as a standalone therapy or in combination.
Calan (Verapamil) and Calan SR are calcium channel blockers. They prevent calcium from entering heart and vessel muscle cells, leading to relaxation and lower blood pressure. Extended-release versions like Calan SR provide once-daily dosing options.
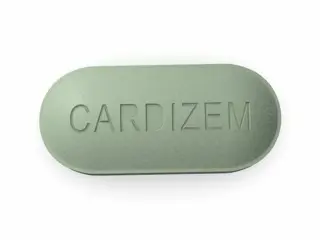
Cardizem (Diltiazem) and Cartia XT are also calcium channel blockers. They are effective for treating hypertension and certain arrhythmias. Slow-release forms allow for stable blood levels and easier adherence.
Catapres (Clonidine) works differently. It stimulates alpha-2 receptors in the brain to reduce sympathetic outflow. It effectively lowers blood pressure but may cause sedation or dry mouth. Withdrawal should be gradual to avoid rebound hypertension.
Combipres is a combination pill that includes an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic. Combining drugs simplifies treatment and improves compliance. It targets blood pressure through multiple pathways.
Coreg (Carvedilol) is a non-selective beta-blocker with additional alpha-blocking effects. It helps lower blood pressure and improve heart function in conditions like heart failure. It may cause dizziness initially but is effective long-term.
Coversyl (Perindopril) is similar to Aceon and Altace in its ACE inhibitory action. It reduces the risk of stroke and heart attack while lowering blood pressure. Patients with a history of cough may need alternative therapies.
Cozaar (Losartan) is a commonly prescribed ARB. It offers robust blood pressure control and kidney protection. Unlike ACE inhibitors, it rarely causes cough, making it a popular choice.
Diltiazem is frequently used in both hypertension and certain heart rhythm disorders. It slows heart rate and dilates blood vessels. Slow-release forms improve patient compliance.
Esidrix (Hydrochlorothiazide) is a thiazide diuretic that helps reduce blood volume by increasing urine output. It is often used as a first-line agent. Patients should monitor electrolyte levels, especially potassium.
Frumil combines a loop diuretic with potassium-sparing elements. It rapidly reduces fluid overload and is useful in resistant hypertension. Close monitoring is essential to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
Hytrin (Terazosin) is an alpha-1 blocker. It relaxes blood vessels and improves urine flow in patients with prostate enlargement. It can cause dizziness, especially on standing, so dose adjustment may be needed.
Hyzaar combines an ARB (Losartan) with a diuretic (Hydrochlorothiazide). This combo tackles blood pressure on two fronts. It improves efficacy and reduces side effects associated with higher doses of single agents.
Inderal (Propranolol) is a non-selective beta-blocker. It reduces heart rate and cardiac output. It is also used for migraine prevention and anxiety in addition to hypertension. Side effects include fatigue and cold extremities.
Inderal LA is a long-acting version of Inderal. It allows for once-daily dosing and steadier blood pressure control. Patient adherence often improves with LA formulations.
Isoptin and Isoptin SR contain Verapamil. They manage hypertension and angina. Slow-release forms help maintain consistent blood levels, making management easier.
Lasix (Furosemide) is a potent loop diuretic used in cases of fluid retention and severe hypertension. It acts quickly to remove excess fluid but can lead to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration if not closely monitored.
Lisinopril is a widely used ACE inhibitor. It offers effective blood pressure reduction and heart protection. Routine kidney and electrolyte checks are necessary to avoid complications.
Lopressor and Toprol (Metoprolol) are beta-blockers often prescribed for hypertension and heart disease. Slow-release forms like Toprol XL improve patient convenience and steady blood pressure control.
Lozol (Indapamide) is a thiazide-like diuretic that reduces fluid retention and dilates blood vessels. It is effective for hypertension and edema due to heart failure or kidney disease.
Micardis (Telmisartan) is an ARB with a long half-life, allowing once-daily dosing. It aids in kidney protection and blood pressure control. It is well tolerated with a low incidence of side effects.
Microzide (Hydrochlorothiazide) is a staple thiazide diuretic. Often combined with other antihypertensives, it helps manage mild to moderate hypertension. Monitoring potassium and sodium levels is crucial.
Minipress (Prazosin) is an alpha-1 blocker. It helps relax blood vessels and improve urine flow. It may cause dizziness, especially during the first days of treatment.
Norvasc (Amlodipine) is a widely used calcium channel blocker. It effectively lowers blood pressure and treats angina. It is generally well tolerated but may cause swelling in the ankles or feet.
Prinivil (Lisinopril) shares many characteristics with other ACE inhibitors. Patients may experience cough, which is a common reason for switching to ARBs.
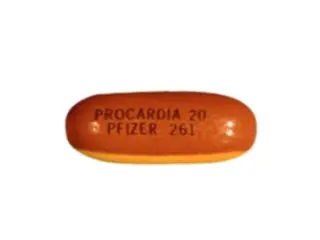
Procardia (Nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker used in hypertension and angina. Extended-release versions reduce the risk of side effects such as rapid heartbeats or flushing.
Tenormin (Atenolol) is a beta-blocker that lowers heart rate and blood pressure. It is less lipid-soluble than some others, which may reduce central nervous system side effects.
Toprol XL offers once-daily metoprolol. It improves patient compliance and provides steady control for hypertension and heart disease.
Trandate (Labetalol) is a combined alpha and beta-blocker. It is effective for severe hypertension and during pregnancy. Blood pressure should be monitored regularly during treatment.
Tritace (Ramipril) is an ACE inhibitor similar to Altace with protective effects for the heart and kidneys. Regular monitoring for side effects is needed.
Vasotec (Enalapril) is another ACE inhibitor choice. It lowers blood pressure and protects heart function. It may cause cough in some patients.
Verampil (Verapamil) is a calcium channel blocker that controls hypertension and arrhythmias. Side effects include constipation and dizziness.
Zebeta (Bisoprolol) is a cardioselective beta-blocker. It lowers heart rate and blood pressure with fewer respiratory side effects. It is often chosen for patients with asthma.
Zestoretic contains lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. This combination improves efficacy with lower doses of each component. It simplifies treatment for many patients.
Zestril (Lisinopril) is a well-known ACE inhibitor. It helps reduce blood pressure and prevents cardiovascular events. Patient monitoring for dry cough or swelling is important.
Choosing the right blood pressure medication depends on the patient's overall health, other medical conditions, and possible side effects. Often, lifelong management and combination therapy are necessary to maintain optimal blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.